Image
Figure Caption
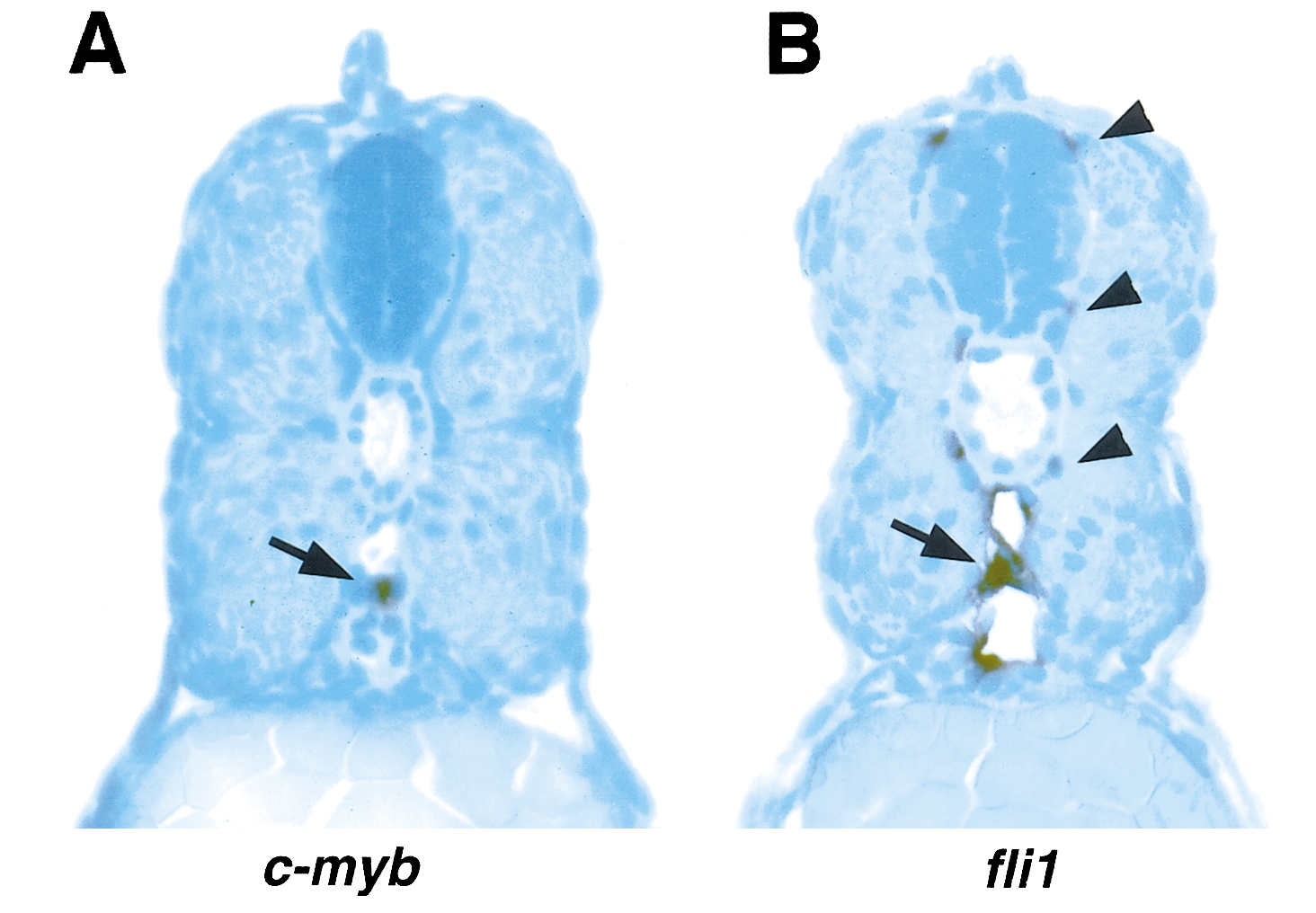
Fig. 4 The relative positions of cells that express c-myb or fli1 in 48-h-old embryos. Cross sections through the trunk of 48-h-old embryos stained for c-myb (A) expression or fli1 (B) expression by whole-mount in situ hybridization. The positive cell in A (arrow) lies in the ventral wall of the dorsal aorta. In B, staining is seen in the endothelial cells (arrow) of the dorsal aorta and caudal vein as well as in regions coinciding with the segmental artery and vein (arrowheads).
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 197, Thompson, M.A., Ransom, D.G., Pratt, S.J., MacLennan, H., Kieran, M.W., Detrich,III, H.W., Vail, B., Huber, T.L., Paw, B., Brownlie, A.J., Oates, A.C., Fritz, A., Gates, MA., Amores, A., Bahary, N., Talbot, W.S., Her, H., Beier, D.R., Postlethwait, J.H., and Zon, L.I., The cloche and spadetail genes differentially affect hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis, 248-269, Copyright (1998) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.