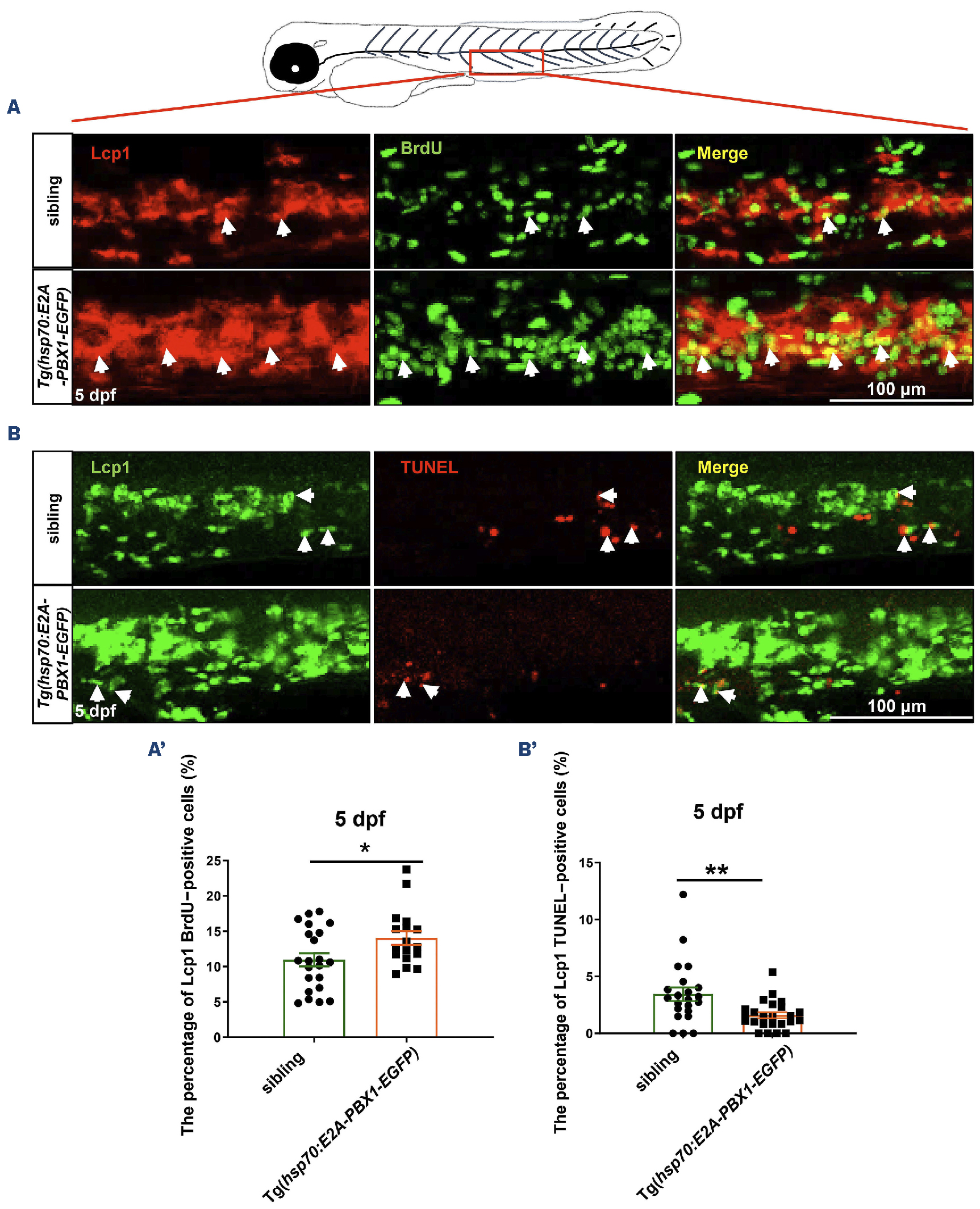
Fig. 3 Abnormal myeloid cell expansion in Tg(hsp70:E2A-PBX1-EGFP) fish caused by proliferation and apoptosis perturbation. (A) Immunofluorescence double staining of Lcp1 and bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) antibodies reveals a significant increase in myeloid cell proliferation in the caudal hematopoietic tissue (CHT) region of 5 days post-fertilization (dpf) Tg(hsp70:E2A-PBX1-EGFP) larvae (N=22) compared with the siblings (N=17). Lcp1/BrdU double-positive cells are indicated by white arrows. (A’) Statistical analysis of percentage of Lcp1+ BrdU+ cells in panel (A). The black asterisks indicate statistical difference (Student t tests, mean ± standard error of the mean; *P<0.05). (B) Co-staining of Lcp1 and transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) was used to detect the apoptosis in the CHT region of 5 dpf Tg(hsp70:E2A-PBX1-EGFP) larvae (N=22) compared with the siblings (N=24). Lcp1/TUNEL double-positive cells are indicated by white arrows. (B’) Statistical analysis of percentage of Lcp1+ TUNEL+ cells in panel (B). The black asterisks indicate statistical difference (Student t tests, mean ± standard error of the mean; **P<0.01).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Haematologica