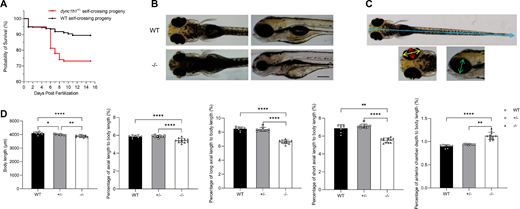
Fig. 2 Impact of dync1h1 loss on zebrafish survival and overall development. (A) Kaplan-Meier survival curve for the progeny of self-crossed WT or dync1h1+/− zebrafish. (B) External morphology of WT and dync1h1+/− zebrafish at 5 dpf. (C) Schematic diagram illustrating measurement indicators at 5 dpf: body length (blue), axial length (red), long axial length (yellow), short axial length (green), and anterior chamber depth (white). (D) Quantitative analysis of binocular measurements as a percentage of body length in WT, dync1h1+/−, and dync1h1−/− zebrafish at 5 dpf. +/−, dync1h1 heterozygote; −/−, dync1h1 homozygote. Scale bar = 200 µm. Data were presented as mean ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001, n = 8 (WT), n = 10 (dync1h1+/−), and n = 12 (dync1h1−/−). dpf, days post fertilization; SD, standard deviation; WT, wild type.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci.