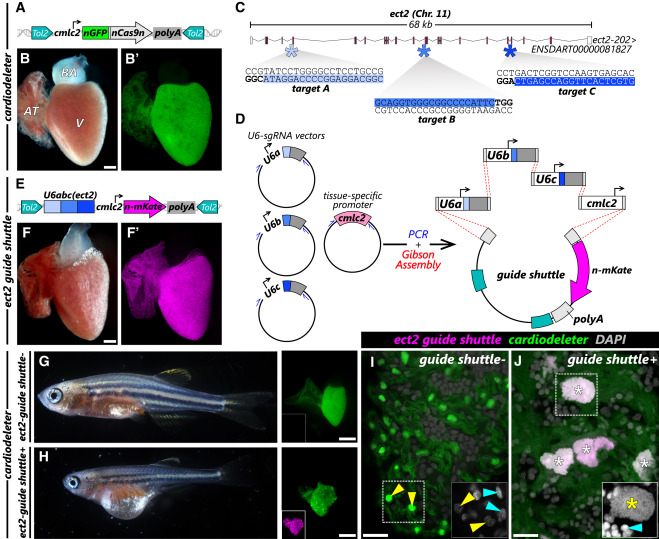
Fig. 1 The cardiodeleter transgene efficiently creates cardiomyocyte-specific LOF phenotypes in combination with gene-specific gRNAs (A) Schematic representation of the cardiodeleter transgene, which drives the expression of nGFP and a zebrafish codon optimized version of Cas9 in cardiomyocytes. (B and B′) Representative heart from an adult zebrafish carrying the cardiodeleter allele, exhibiting normal morphology (B) and expression of nGFP (B′). (C) Representation of the ect2 locus in the zebrafish genome. Filled boxes represent coding exons, empty boxes indicate the 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR. Asterisks indicate the location of the three selected gRNA targets, predicted using CRISPRScan. Blue areas indicate the target sequence. Sequences in bold highlight the PAM. (D) Strategy to generate a guide shuttle carrying three U6 promoters (U6a, U6b, and U6c), each driving the expression of a gRNA targeting a GOI, and a transgenesis reporter. (E) Representation of the stable ect2 guide shuttle transgene. (F and F′) Representative heart from an adult zebrafish carrying the ect2 guide shuttle exhibiting normal morphology (F) and expression of n-mKate (F′). (G and H) The 30-dpf cardiodeleter+ (G) and cardiodeleter+ect2 guide shuttle+ (H) animals. Stalled growth and edema can be observed only in double transgenic animals. (Right) Dissected hearts. (I and J) Confocal images of DAPI-stained whole hearts from 30-dpf cardiodeleter+ (K) and cardiodeleter+ect2 guide shuttle+ (L) animals. Boxed regions show DAPI staining at higher magnification (white). Asterisks: polyploid nuclei. Cyan and yellow arrowheads: non-myocytes and cardiomyocytes, respectively. AT, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; Chr, chromosome; V, ventricle. Scale bars, 200 μm (B and F) and 20 μm (I and J).
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Cell Rep Methods