Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101123-65
- Publication
- Chung et al., 2010 - Suppression of Alk8-mediated Bmp signaling cell-autonomously induces pancreatic β-cells in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
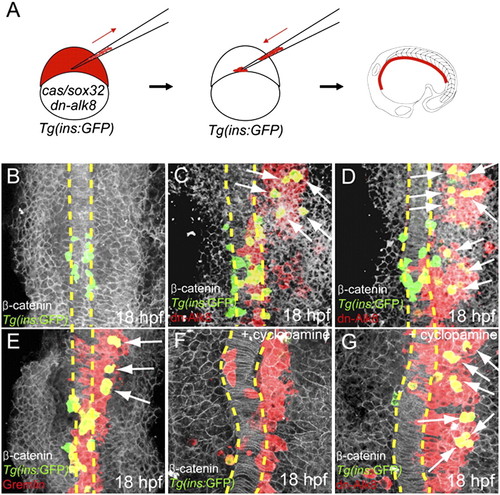
Suppression of Bmp signaling is sufficient to induce ectopic dorsal bud-derived pancreatic β-cells cell-autonomously. (A) Schematic diagram of the cell transplantation protocol. Tg(ins:GFP) donors were injected with cas/sox32 and dn-alk8 RNA along with rhodamine dextran (red), and the cells were transplanted into Tg(ins:GFP) hosts. (B–E) Ventral confocal images of Tg(ins:GFP) (green), β-catenin (white), and rhodamine dextran (red) at 18 hpf (the notochord is outlined by yellow dashed lines). (B) In control embryos, Tg(ins:GFP)-expressing cells are located close to the notochord. (C and D) Ectopic Tg(ins:GFP)-expressing cells (arrows) were found in lateral and anterior endodermal regions where dn-Alk8-expressing cells had incorporated, and all these ectopic cells were donor derived. (E) Gremlin1a overexpression in the endoderm also resulted in the ectopic formation of Tg(ins:GFP)-expressing cells (arrows). (F) When Hedgehog signaling was blocked with cyclopamine, Tg(ins:GFP)-expressing cells were almost absent in hosts containing control donor cells. (G) dn-Alk8 expression still induced the formation of Tg(ins:GFP)-expressing cells (arrows) even after cyclopamine treatment, and it did so cell-autonomously. |