FIGURE
Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111026-18
- Publication
- Lu et al., 2011 - Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell growth by tbx5 knockdown contribute to dysmorphogenesis in Zebrafish embryos
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. 6
|
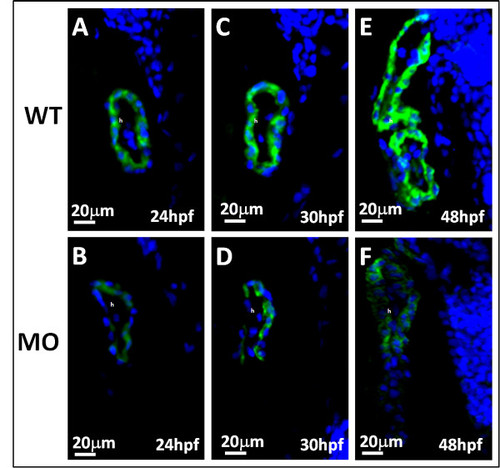
Myosin of zebrafish embryos was stained by the heart-specific anti-myosin antibody, MF20 (green), and counterstained by DAPI (blue) for nuclear observation. A-F: The expression of MF20 in embryos with tbx5 deficiency (B, D, F) decreased throughout the developmental stages compared to that in the WT (A, C, E), from 24 to 48 hpf. The anterior of embryos is to the left. h, heart; MO, tbx5-MO-treated embryos. |
Expression Data
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Long-pec |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ J. Biomed. Sci.