Figure 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-230331-23
- Publication
- Buglak et al., 2023 - Nuclear SUN1 stabilizes endothelial cell junctions via microtubules to regulate blood vessel formation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
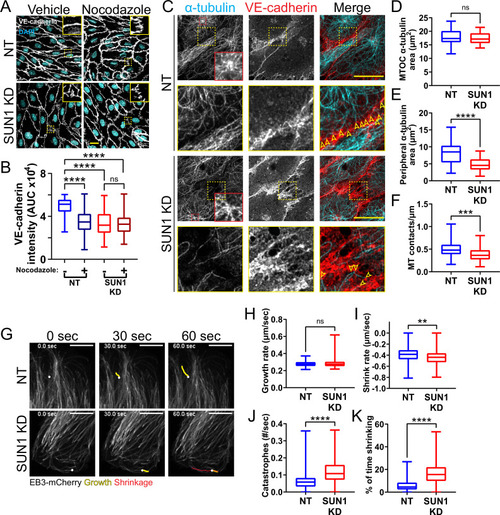
(A) Representative images of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) with indicated siRNAs and indicated treatments. Endothelial cells were stained for DAPI (cyan, DNA) and VE-cadherin (white, junctions). Insets show junctions. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Quantification of VE-cadherin line scans for treatments shown in (A). n=106 junctions (non-targeting [NT], vehicle), 101 junctions (NT, Nocodazole), 105 junctions (SUN1 knockdown [KD], vehicle), and 96 junctions (SUN1 KD, Nocodazole) compiled from three replicates. ns, not significant; ****, p<0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (C) Representative images of HUVEC with indicated siRNAs. Endothelial cells were stained for α-tubulin (cyan, microtubules) and VE-cadherin (red, junctions). Red insets show α-tubulin at the MTOC (microtubule organizing center), yellow insets show α-tubulin contacts at junctions. Arrows denote contact sites. Scale bar, 20 µm. (D) Quantification of α-tubulin area at the MTOC shown in (C). n=19 cells (NT) and 10 cells (SUN1 KD) compiled from three replicates. ns, not significant by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. (E) Quantification of peripheral α-tubulin area shown in (C). n=39 cells (NT) and 46 cells (SUN1 KD) compiled from three replicates. ****, p<0.0001 by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. (F) Quantification of contacts between α-tubulin and VE-cadherin shown in (C). n=75 junctions (NT) and 48 junctions (SUN1 KD) compiled from three replicates. ***, p<0.001 by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. (G) Stills from Video 5 and Video 6 showing microtubule growth in EB3-mCherry labeled HUVEC. White dot indicates start of track. Yellow line indicates growth, red line indicates shrinkage. Scale bar, 10 µm. (H) Quantification of microtubule growth rate from EB3-mCherry microtubule tracking. N=120 microtubules (12 cells, NT) and 117 microtubules (12 cells, SUN1 KD) compiled from two replicates. ns, not significant by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. (I) Quantification of microtubule shrink rate from EB3-mCherry microtubule tracking. n=120 microtubules (12 cells, NT) and 117 microtubules (12 cells, SUN1 KD) compiled from two replicates. **, p<0.01 by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. (J) Quantification of catastrophe rate from EB3-mCherry microtubule tracking. n=120 microtubules (12 cells, NT) and 117 microtubules (12 cells, SUN1 KD) compiled from two replicates. ****, p<0.0001 by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. (K) Quantification of percent of time spent shrinking from EB3-mCherry microtubule tracking. n=120 microtubules (12 cells, NT) and 117 microtubules (12 cells, SUN1 KD) compiled from two replicates. ****, p<0.0001 by Student’s two-tailed unpaired t-test. For all graphs, boxes represent the upper quartile, lower quartile, and median; whiskers represent the minimum and maximum values.
|