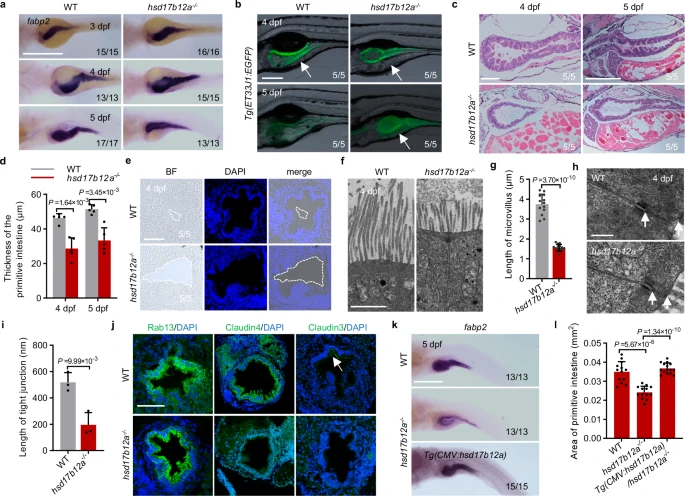
Fig. 4 The primitive intestinal structures exhibit defects.a Intestinal development was examined using whole-mount in situ hybridization in both WT and hsd17b12a−/− at 3 dpf, 4 dpf, and 5 dpf (n > 3). Scale bar, 200 μm. b Intestinal fluorescence imaging of WT and hsd17b12a−/− (n = 5). The white arrows indicate the yolk region. Scale bar, 200 μm. c HE staining of paraffin sections of the intestine in hsd17b12a−/− and WT at 4 dpf and 5 dpf (n = 5). Scale bar, 100 μm. d The thickness of the primitive intestine was quantified in WT and hsd17b12a−/− at 4 dpf and 5 dpf. e Confocal imaging of the intestine in WT and hsd17b12a−/− at 4 dpf (n = 5). The white dotted line indicates the intestinal lumen. Scale bar, 100 μm. f, g Transmission electron microscopy micrographs (TEM) (n > 3) and quantification of the intestinal microvilli length in WT and hsd17b12a−/− at 4 dpf. Scale bar, 0.5 μm. h, i TEM micrographs (n = 3) and quantification of the intestinal tight junction length in WT and hsd17b12a−/− at 4 dpf. The white arrows indicate the tight junctions. Scale bar, 0.5 μm. j Immunofluorescence staining of proteins associated with tight junction formation in the intestine of WT and hsd17b12a−/− at 4 dpf (n = 3). Scale bar, 50μm. k Tg(CMV:hsd17b12a) rescued the expansion defects of primitive intestine in hsd17b12a−/− (n ≥ 3). Scale bar, 0.5 mm. l The area of the primitive intestine was quantified by the signal of fabp2 in WT, hsd17b12a−/− and Tg(CMV:hsd17b12a)/hsd17b12a−/−. Data in d, j, i, l are represented as mean ± S.D., using a two-tailed Student’s t test; each point represents an independent biological sample (n ≥ 3). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Nat. Commun.