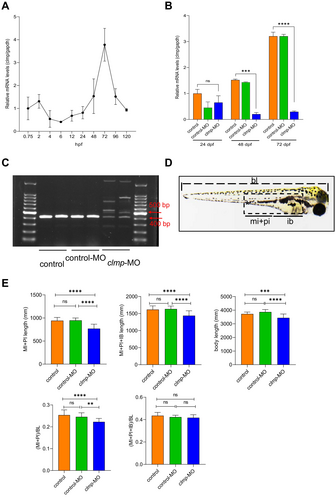
Fig. 2 Clmp knockdown caused developmental defects during zebrafish embryogenesis. (A) The qRT-PCR analysis of relative expression levels of clmp in zebrafish embryos from 0.75 hpf to 120 hpf. (B) The qRT-PCR analysis of relative expression levels of clmp in control, control-MO, and clmp-MO zebrafish embryos at 24 hpf, 48 hpf, and 72 hpf (each group, n = 3). (C) The efficacy of clmp SBMO was confirmed by RT-PCR in embryos at 72 hpf. The larger products were observed when clmp SBMO was injected into the embryos (each group, n = 2). (D) Measurement of zebrafish body length. ib., intestinal bulb; mi, mid-intestine; pi, posterior intestine; *anal opening. (E) Statistical analysis of all groups' average body and gut lengths at 72 hpf. control(n = 16) versus control-MO (n = 16) versus clmp-MO (n = 22). clmp-MO, clmp morpholino group; control-MO, control morpholino group; SBMO, splice-blocking morpholino oligonucleotide; untreated group. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Clin. Genet.