- Title
-
Loss-of-Function of CLMP Is Associated With Congenital Short Bowel Syndrome and Impaired Intestinal Development
- Authors
- Chen, S., Xu, J., Xiao, Y., Cai, H., Zhou, J., Cai, W., Wang, Y.
- Source
- Full text @ Clin. Genet.
|
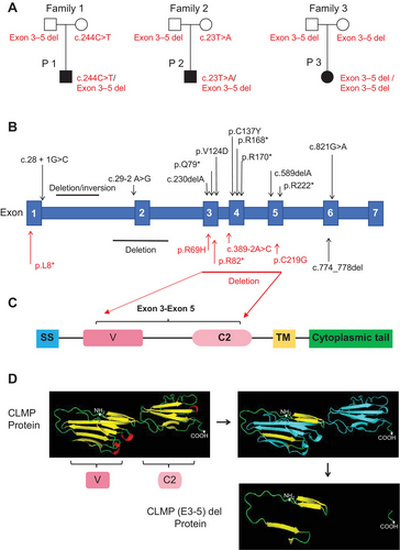
Genetic analysis of CSBS patients. (A) Pedigree of the three families in this study with CLMP genetic mutations. (B) Schematic overview of all the variants identified in the human CLMP gene that coincide with CSBS. In red are the variants reported in our center and in black are the variants previously described. Numbering starts with position 1 at the amino-terminal methionine of the unprocessed polypeptide. The single letter code for amino acids is used, with one asterisk (*) indicating translation stop. (C) Schematic diagram of human CLMP protein structures. C2, C2-typed Ig-loops; SS, signal sequence; TM, transmembrane region; V, V-typed Ig-loops. (D) Crystal structure of the extracellular region of CLMP protein tertiary structure was calculated by Phyre2 based on CAR (PDB: 3jz7A) as the template for molecular modeling. The CLMP Model dimensions (Å): X:60.895 Y:40.957 Z:82.390. The asterisks mark the amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal. The blue region represents the corresponding amino acid sequence of exons 3–5. CAR, coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor. |
|
Clmp knockdown caused developmental defects during zebrafish embryogenesis. (A) The qRT-PCR analysis of relative expression levels of clmp in zebrafish embryos from 0.75 hpf to 120 hpf. (B) The qRT-PCR analysis of relative expression levels of clmp in control, control-MO, and clmp-MO zebrafish embryos at 24 hpf, 48 hpf, and 72 hpf (each group, n = 3). (C) The efficacy of clmp SBMO was confirmed by RT-PCR in embryos at 72 hpf. The larger products were observed when clmp SBMO was injected into the embryos (each group, n = 2). (D) Measurement of zebrafish body length. ib., intestinal bulb; mi, mid-intestine; pi, posterior intestine; *anal opening. (E) Statistical analysis of all groups' average body and gut lengths at 72 hpf. control(n = 16) versus control-MO (n = 16) versus clmp-MO (n = 22). clmp-MO, clmp morpholino group; control-MO, control morpholino group; SBMO, splice-blocking morpholino oligonucleotide; untreated group. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
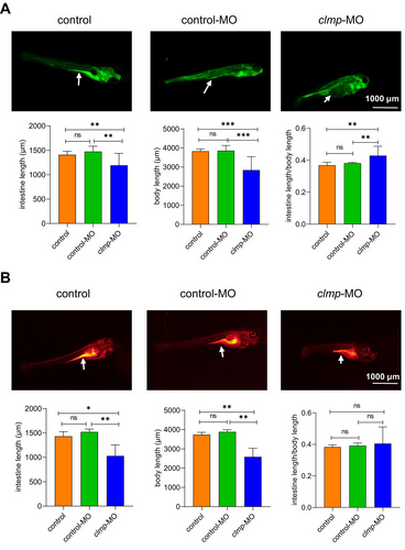
Clmp knockdown of zebrafish caused gastrointestinal motility disorder. In vivo imaging of zebrafish digestive organ with fluorescent reporters and statistical analysis of all groups' average body lengths and gut lengths. (A) 0.2% Calcein solution for 10 min at 28.5°C. Arrowheads indicate intestine; control group, n = 12; control-MO group, n = 5; clmp-MO group, n = 16. (B) 20 μg/mL Nile Red solution for 16 h at 28.5°C (each group, n = 6). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant. All scar bars: 1000 μm. clmp-MO, clmp morpholino group; control group; control-MO, control morpholino group; untreated group. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
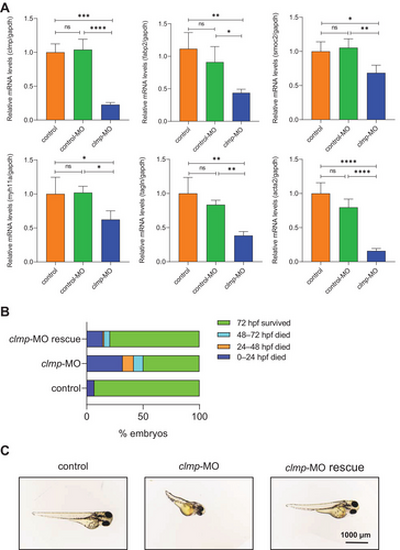
Clmp knockdown decreased smooth muscle-related gene expression in Zebrafish, and clmp mRNA partly rescued the knockdown phenotype in zebrafish embryos. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of the mRNA levels of clmp, fabp2, smoc2, myh11a, tagln, and acta2 expression in zebrafish embryos of control, control-MO, and clmp-MO groups at 72 hpf (each group, n = 3–6). The expression of gapdh gene was used as an internal control. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. (B) The mortality rate of embryos with clmp-MO injection, clmp-MO, and clmp mRNA con-injection during different embryonic stages. (C) Gross morphology of zebrafish embryos at 72 hpf in three groups. Most embryos con-injected with clmp-MO and clmp mRNA were morphologically normal, whereas those injected showed growth defects. acta2, actin alpha 2; clmp-MO, clmp morpholino group, clmp-MO rescue group, co-injection of clmp morpholino and clmp mRNA group; control group, untreated group; control-MO, control morpholino group; Fabp2, fatty acid binding protein 2; myh11, myosin, heavy chain 11a; smoc2, SPARC-related modular calcium binding 2; tagln, transgelin. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|