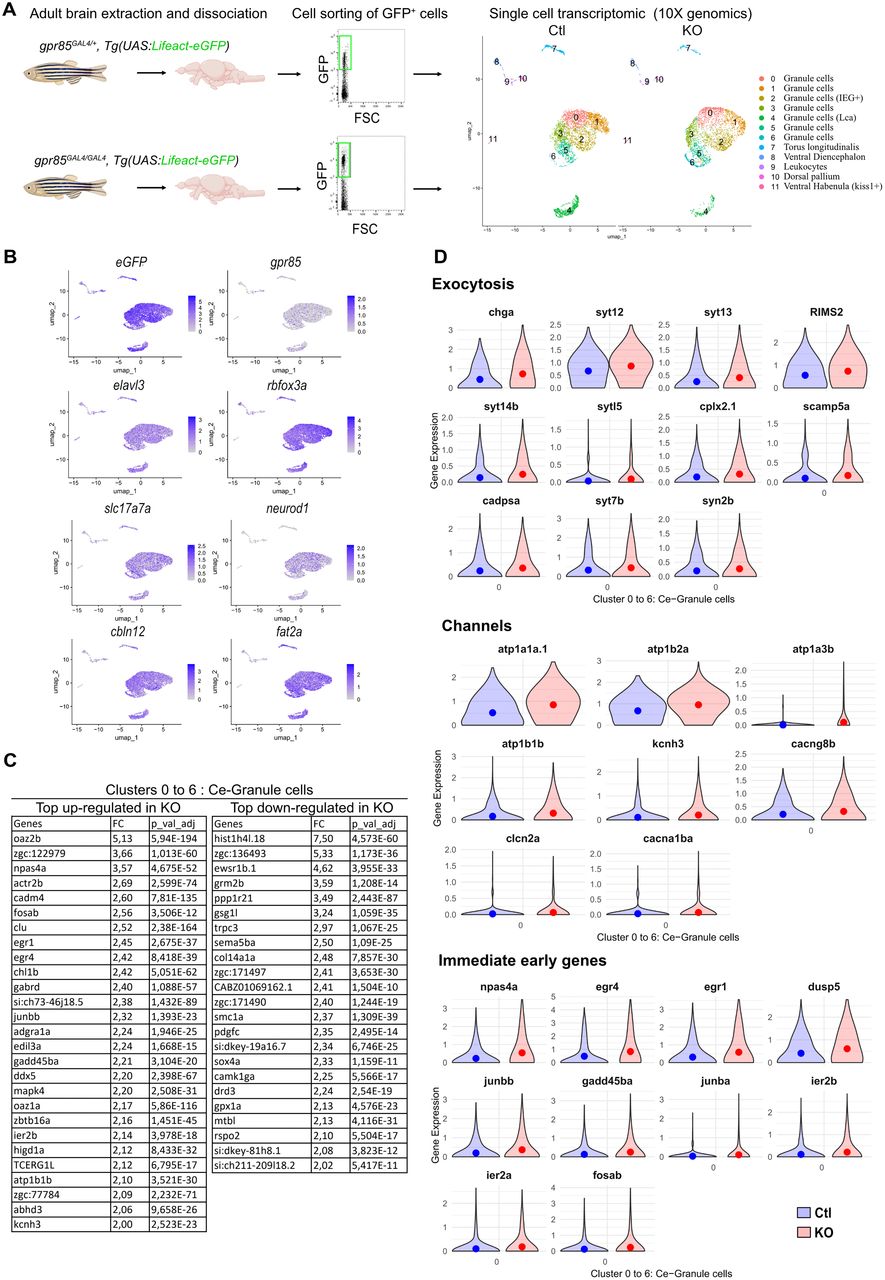
Fig. 6 scRNAseq analysis of eGFP+ sorted cells from adult gpr85GAL4/+ and gpr85GAL4/GAL4, Tg(UAS:lifeact-eGFP) dissociated brains reveals changes in gene expression related to neuronal activity. A, Experimental strategy for assessing transcriptomic changes in gpr85-expressing cells from the Gpr85-deficient adult brain. GFP+ cells were sorted from gpr85GAL4/+ (Ctl) and gpr85GAL4/GAL4 (KO), Tg(UAS:lifeact-eGFP) dissociated brains (cell sorting strategy shown with 10,000 events per condition). The right panel shows the UMAPs of cells from the Ctl and KO conditions (n = 4,219 cells and n = 3,341 cells, respectively) after filtering and clustering. B, UMAPs of Ctl and KO cells merged, displaying expression of the UAS:lifeact-eGFP transgene, gpr85, the two pan-neuronal markers elavl3 and rbfox3a, as well as the expression of the GC markers, sls17s7a, neurod1, cbln12, and fat2a. C, Table of the most up- and downregulated genes within the isolated cerebellar clusters (0 to 6) in the KO condition, with a minimal FC of two and an adjusted p < 10−4, expressed by at least 6% of the cells. D, Violin plots of most significantly DEGs with a minimal FC of 1.4 and an adjusted p < 10−4. All genes referenced are upregulated (mean represented by the dots). Top panel, Selection of genes related to exocytosis. Intermediate panel, Selection of genes encoding channels related to neuronal excitability/activity (voltage-dependent channels, clcn2a, cacna1ba, kcnh3, cacng8b; Na+/K+ ATPase subunits, atp1a3b, atp1b1b, atp1a1a.1, atp1b2a, syn2b). Lower panel, genes documented as IEGs.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ J. Neurosci.