- Title
-
A novel loss-of-function mutation in NRAP is associated with left ventricular non-compaction cardiomyopathy
- Authors
- Zhang, Z., Xu, K., Ji, L., Zhang, H., Yin, J., Zhou, M., Wang, C., Yang, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cardiovasc Med
|
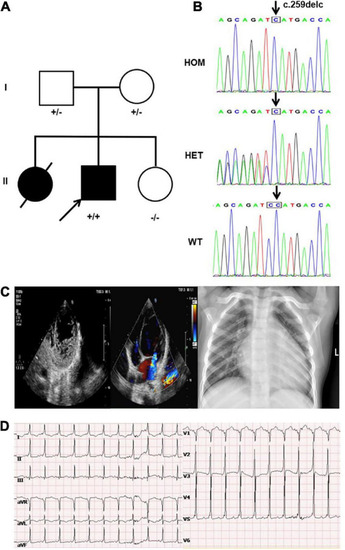
Clinical and genetic findings. (A) Pedigree: the proband was indicated by an arrow. The presence or absence of the nebulin-related-anchoring protein (NRAP) variant is indicated by a ± symbol. (B) Identification of a homozygous mutation NRAP frameshift mutation c.259delC in the proband inherited from his father and mother. (C) Echocardiogram showed an enlarged left atrium and ventricle of the heart, prominent trabecular meshwork, and deep intertrabecular recesses. Chest X-ray of the proband showed an enlarged left ventricular (LV) cavity. (D) The ECG revealed sinus tachycardia, ventricular pre-excitation, and T-wave changes in some leads. |
|
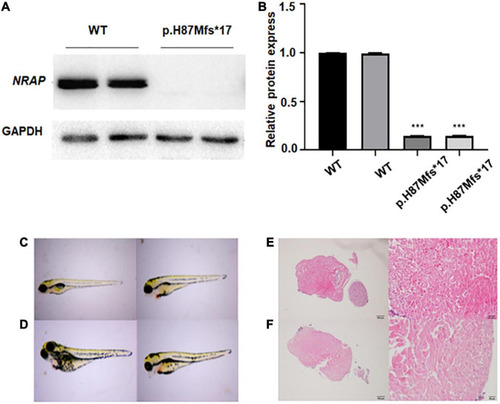
Functional study of p.H87Mfs*17 mutation in nebulin-related-anchoring protein (NRAP). (A) Total cell protein expressions of wild-type (WT) vs. the mutated NRAP determined by Western blotting. p.H87Mfs*17 mutation led to decreased expression of NRAP. (B) Quantitative analysis of total cell protein expressions of WT vs. mutated NRAP. All values are means ± SD; n = 6 in each group. ***P < 0.001 vs. control. (C,D) Images of juvenile fish with pericardial edema. Two cases were the wild-type (WT) zebrafish (C) and two cases carried a homozygous mutation of the NRAP allele (D). (E) HE-stained heart tissue of normal zebrafish. (F) HE-stained heart tissue of zebrafish with pericardial edema. PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements |