- Title
-
In silico and in vivo analyses of a novel variant in MYO6 identified in a family with postlingual non-syndromic hearing loss from Argentina
- Authors
- Buonfiglio, P.I., Bruque, C.D., Salatino, L., Lotersztein, V., Pace, M., Grinberg, S., Elgoyhen, A.B., Plazas, P.V., Dalamón, V.
- Source
- Full text @ NAR Genom Bioinform
|
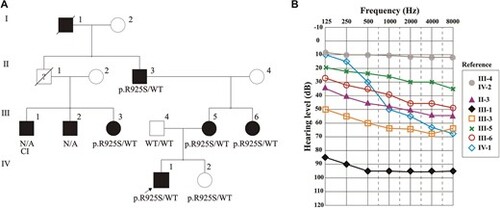
(A) Pedigree of the family harboring the causative variant p.Arg925Ser located within exon 26 of the MYO6 gene. Whole-exome sequencing was conducted on the proband IV-1, indicated by the arrow. All individuals with hearing impairment are in black. Seven members referred progressive postlingual hearing impairment (five available for the study), compatible with a dominant mode of inheritance. The genetic status ‘WT’ indicates wild type, ‘NA’: not available. (B) Audiograms of the affected family members who participated in the genetic test are shown, revealing the variable expressivity of the pathology. The patient's mother (III-5) and three aunts (III-1, III-3 and III-6) presented mild-moderate to severe and profound postlingual hearing impairment with onset in their thirties. They were all equipped with hearing aids, except III-1 that was cochlear implanted ‘CI’. |
|
(A) Representative alignment across six MYO6 orthologous chordate sequences, revealing a 100% sequence identity for the Arg925 residue. (B) Structural modeling analysis of the IQ domain (pink), the three-helix bundle (orange) and the SAH (grey). (C) Evaluation of patterns on the protein surface showing the change in the electrostatic charge (arrow). Details of the interactions of the p.Arg925 or Ser925 within the SAH domain. The distances between p.Arg925 and p.Glu921/p.Glu922 are indicated as sticks in surface residues. (D) Schematic representation of MYO6 with the motor domain, neck domain and tail region. Residue numbers correspond to human MYO6, Uniprot entry Q9UM54. |
|
Morphological analysis of myo6b knockdown in zebrafish at 5 dpf: (A) lateral view of a larva with a wild-type phenotype, (B) lateral view of a myo6b morphant. Knockdown of myo6b caused non-inflation of the swim bladder. (C) Spider chart showing the percentages of the two variables analyzed: inflated and non-inflated swim bladder for each condition: WT, MO-CON, MO, MO-WT-mRNA, MO-R925S-mRNA. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
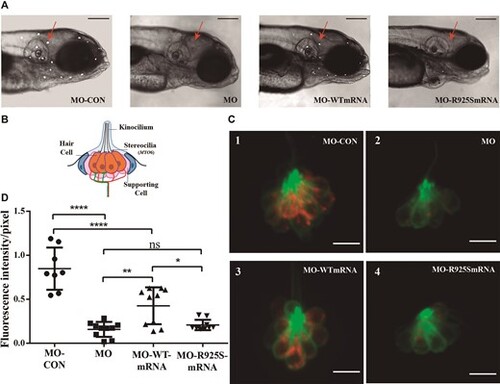
In vivo rescue assay of myo6b MO phenotype with human mRNAs. Coinjection of human wild-type MYO6 mRNA with myo6b MO resulted in partial rescue of the knockdown phenotype, whereas co injection of MO and human MYO6 mRNA with the c.2775G>C p.Arg925Ser novel variant (MO-p.R925S-mRNA) was unable to rescue the knockdown phenotype. (A) Lateral views of the head of 5dpf larvae labeled with 4-Di-2-Asp (10X magnification). Neuromasts stained are shown as white dots. Red arrows point at neuromasts situated between the otic vesicle and the eye, where fluorescence intensity measurements were performed. Scale bar: 200 μm. (B) Schematic depicts a lateral view of a neuromast. (C) Confocal images showing the uptake of 4-Di-2-Asp (red) by LL hair cells of 5 dpf Tg (Brn3c:GFP) larvae. GFP (green) is expressed in neuromast hair cells. Scale bar: 9 μm. (D) Box and whisker plot: fluorescence intensity per pixel (F/pix) normalized to the fluorescence intensity of non-injected larvae. ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparison-test,: ****P < 0.0001, ***P< 0.001, **P< 0.01, *P < 0.05, n = 10 neuromasts from five larvae, for each group. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|