Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250305-23
- Publication
- Ma et al., 2025 - Establishment and application of a zebrafish model of Werner syndrome identifies sapanisertib as a potential antiaging drug
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
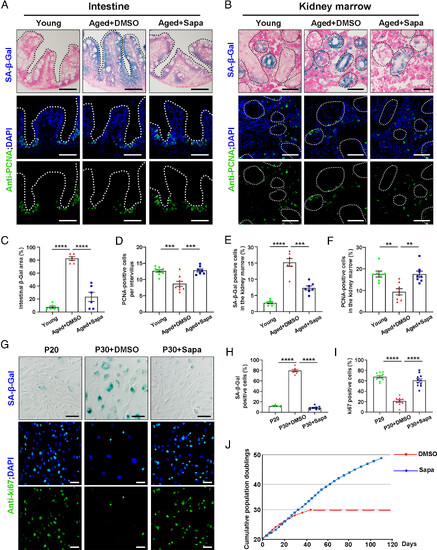
Sapanisertib alleviated aging phenotypes in both physiological-aging zebrafish and replicative-senescent HFF. (A and B) Representative images of SA-β-Gal staining (Top) and immunofluorescence sections images of proliferation staining (PCNA, Bottom) in the intestine (A) and kidney marrow (B) of young, aged+DMSO, and aged+Sapa groups. (C–F) Quantification of the percent of SA-β-Gal positive area in the intestine (C, n = 6 for each group) and kidney marrow (E, n = 7 for each group). Quantification of the PCNA-positive cells per intervillus in the intestine (D, n = 7 to 9 for each group) and the percent of PCNA-positive cells among kidney marrow (F, n = 7 to 8 for each group). (G) Representative image of SA-β-Gal staining and immunofluorescence images of proliferation staining (ki67) in HFF cells of P20, P30+DMSO, and P30+Sapa groups. (H and I) Quantification of the percent of SA-β-Gal staining positive cells (H, n = 7 to 8 for each group) and the percent of ki67 positive cells (I, n = 9 to 11 for each group) in HFF cells. (J) The total cumulative population doublings of HFF cells in standard conditions (DMSO) and in sapanisertib treatment are depicted. Each dot denotes a passage, and the dashed line indicates the cessation of cell expansion. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. HFF, human foreskin fibroblasts; PCNA, proliferation cell nuclear antigen; P20, passage 20. |