- Title
-
Further delineation of defects in MRPS2 causing human OXPHOS deficiency and early developmental abnormalities in zebrafish
- Authors
- Kandettu, A., Yeole, M., Sekar, H., Garapati, K., Kaur, N., Anand, A., Hegde, P., Nair, K., Medishetti, R., Bhat, V., Radhakrishnan, P., Mundkur, S.C., Shrikiran, H.A., Pandey, A., Sevilimedu, A., Chakrabarty, S., Shukla, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Eur. J. Hum. Genet.
|
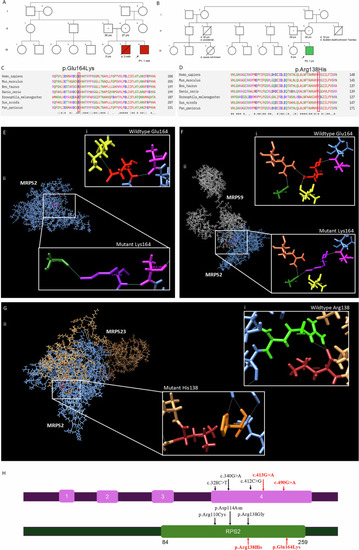
Details of family history and variants in Pedigree of ( |
|
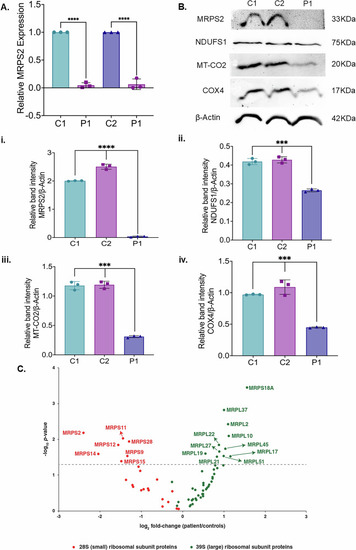
Analysis of MRPS2 expression and OXPHOS proteins in controls and P1 patient derived cells. |
|
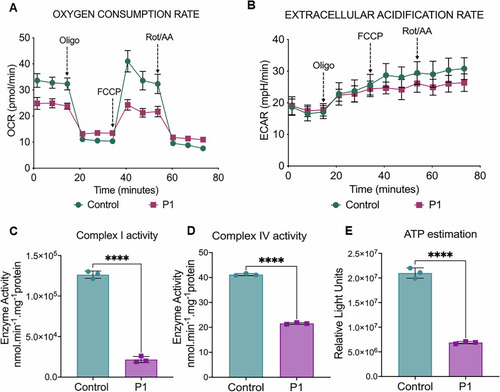
Analysis of mitochondrial OCR and EACR in control and patient fibroblast cells. |
|
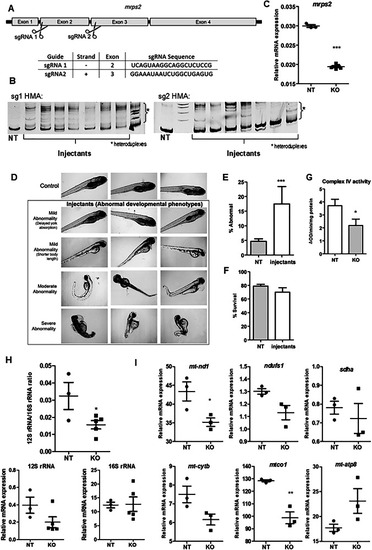
Phenotypes in the |