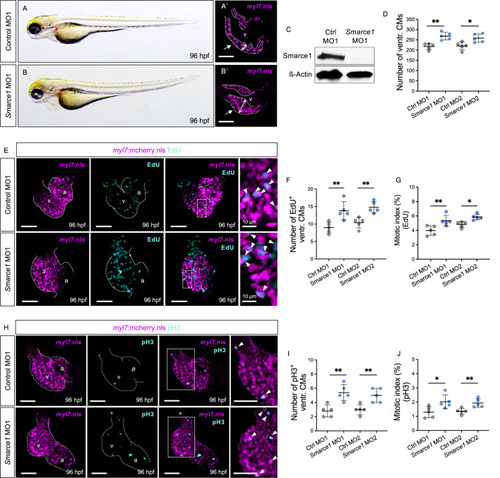
Knockdown of zebrafish smarce1 phenocopies hos cardiac hyperplasia. (A,B) Lateral views of control morpholino (MO; ctrl MO1) or smarce1 start MO (smarce1 MO1)-injected embryo at 96 hpf. Knockdown of smarce1 phenocopies the hos mutant phenotype, whereas the injection of specific control MO does not. (A′,B′) Dissected hearts from Tg (myl7:mcherry.nls) embryos after control or smarce1 MO1 injection (scale bar: 50 µm). Smarce1 knockdown results in a thickened ventricular wall of developing zebrafish heart at 96 hpf. (C) Smarce1 protein is absent in smarce1 MO1-injected embryos at 96 hpf. (D) Quantitative analyses of ventricular CM numbers show a significant increase in the hearts of smarce1 MO1- or MO2-injected embryos at 96 hpf (n = 5). (E) Confocal images of dissected hearts from control- or smarce1 MO1-injected embryos with EdU incorporation displaying CM nucleus (mCherry) and proliferating CMs (cyan) at 96 hpf (scale bar: 50 µm). (F,G) Numbers of EdU+ CMs and the mitotic index are significantly enhanced in smarce1 MO-injected embryonic ventricles compared to control (ctrl) MO-injected hearts at 96 hpf (n = 5). (H) IF images of smarce1 morphant (MO1) heart with pH3 staining displaying CM nucleus (mCherry) and proliferating CMs (cyan) at 96 hpf (scale bar: 50 µm). (I,J) Statistical assessment of counting pH3+ ventricular CMs and the mitotic index in wt and hos at 96 hpf after the injection of specific control MO1/2 or smarce1 MO1/2 reveals increased proliferation in zebrafish embryonic ventricles by the knockdown of smarce1(n = 5). v, ventricle; a, atrium; ventr., ventricular.
|

