- Title
-
The glucocorticoid receptor is affected by its target ZBTB16 in a dissociated manner
- Authors
- Galuh, S., Faught, E., Klaassen, I., Koorneef, L.L., Brinks, J., van Dijk, E.H., Elewaut, D., Schlingemann, R.O., Schaaf, M.J.M., Boon, C.J., Meijer, O.C.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Endocrinol.
|
Cortisol, via GR, enhances endothelial barrier integrity, and this effect is exaggerated after |
|
|
|
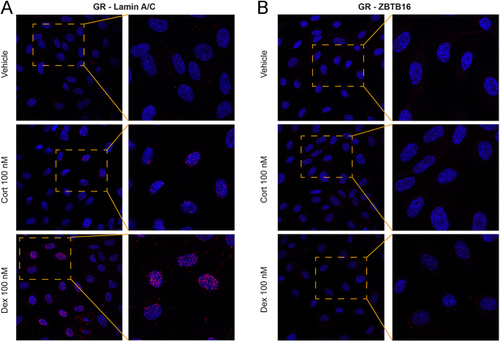
Minimal detection of GR and ZBTB16 close proximity. Primary HUVECs pooled from five donors were treated with either vehicle, 100 nM cortisol (Cort), or 100 nM dexamethasone (Dex). PLA was performed after the cells were probed with primary antibodies. (A) As positive control, Cort and Dex increased the PLA signal (red dots) for GR and Lamin A/C in the nuclei. (B) In the cells probed with antibodies against GR and ZBTB16, Dex but not Cort showed a very modest PLA signal. |
|
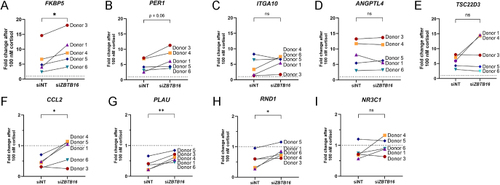
Modulation of GR-mediated transactivation and transrepression of genes by |
|
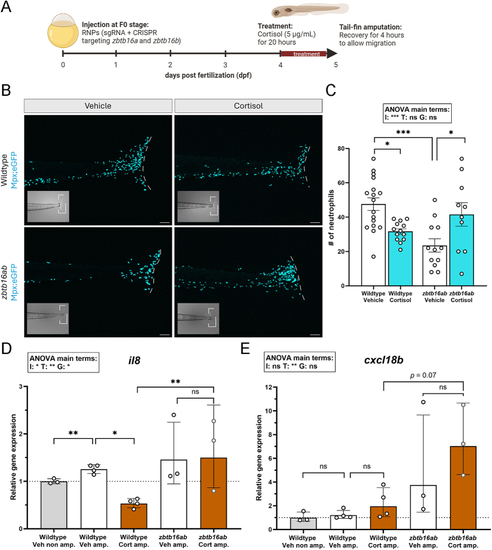
Larvae lacking |
|
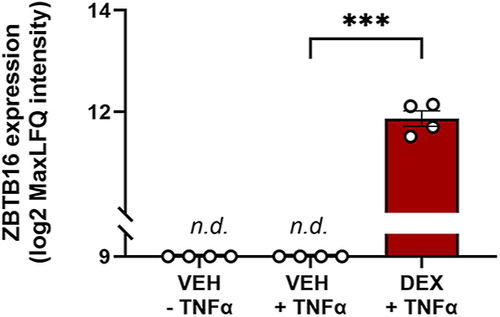
Dexamethasone upregulates ZBTB16 protein expression in FLS derived from osteoarthritis patients. ZBTB16 protein was detected in patient-derived FLS only after treatment with dexamethasone (Dex) (adj. |
|
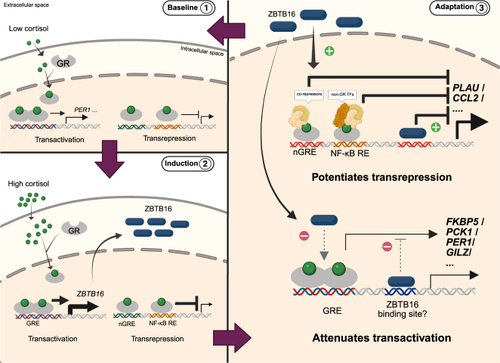
Schematic figure of cortisol-induced ZBTB16 as part of intracellular feedback regulation of GR signaling. Baseline 1: Under low cortisol baseline condition, there is low basal GR transcriptional activity. Induction 2: Under stimulated (high cortisol) conditions, GR induces target genes via transactivation, including |