Figure 2.
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-231031-18
- Publication
- Liu et al., 2023 - Identification of an adverse outcome pathway (AOP) for chemical-induced craniofacial anomalies using the transgenic zebrafish model
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
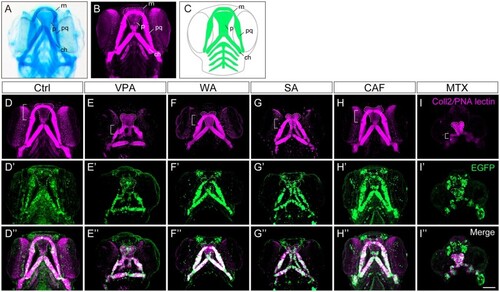
Craniofacial anomalies were identified in teratogen-treated |