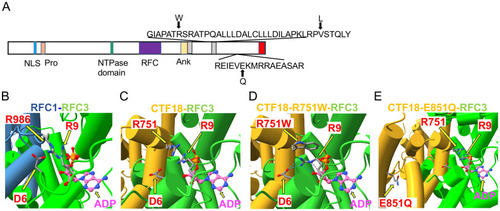
Structural analysis of CHTF18 patient variants.(A) The structure of human CTF18 is schematized with the structural domains and the location of variants inherited from the mother and father indicated above and below the diagram, respectively (52). NLS, nuclear localization signal; Pro, proline-rich domain; Ank, ankyrin repeat domain; TBD, triple barrel domain in red where CTF18 interacts with DSCC1 and CTF8 (53). (B-E) Clamp loader interface of either RFC1 or CTF18 with RFC3. (B) RFC1 structure (PDB #6VVO) shown in blue cylinders for helices and RFC3 in green. The ADP molecule (displayed with pink carbon atoms) bound by RFC3 is shown in ball-and-stick representation, and the key residues RFC1-986 and RFC3-R9 are labeled. (C) AF3 model of CTF18 (gold; residues 583-863) bound to RFC3. The wildtype R751 makes contact with RFC3-R9 in a similar manner compared to RFC1-R986. (D) AF3 model of the R751W variant makes more extensive contacts with RFC3-R9, changing the RFC-R9 rotamer conformation to where it makes 4 hydrogen bonds with RFC-D6 and the 3’ hydroxyl of ADP. (E) AF3 model of the CTF18-E851Q variant in a solvent exposed location distal from the RFC3 interface.
|