Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250917-59
- Publication
- Tevar et al., 2025 - Zebrafish adamtsl4 knockout recapitulates key features of human ADAMTSL4-related diseases: a gene involved in extracellular matrix organization, cell junctions and development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
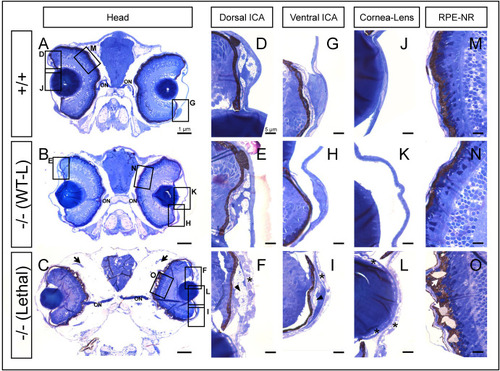
Histological analysis of toluidine blue-stained tissue sections from adamtsl4 KO zebrafish larvae (6 dpf). Transverse semithin tissue sections (500 nm) were prepared as described in the Materials and Methods section. Representative photographs of wild type (+/+), wild type-like KO (−/− (WT-L)) and lethal KO (−/− (Lethal)) larvae are shown. A-C. Tissue sections from the central part of the eyeball (note the presence of the optic nerve (ON)); rectangles indicate areas magnified in subsequent panels. D-F. Dorsal iridocorneal angle (ICA). G-I. Ventral ICA. J-L. Cornea and lens. M-O. Retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE)-neuroretina (NR) interphase. Asterisks: abnormal intercellular separations; black arrows: periocular edema; black arrowhead: increased xantophores; white arrows: amorphous deposits in the RPE. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.) |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 6 |
Reprinted from Experimental Eye Research, , Tevar, A., Aroca-Aguilar, J.D., Atiénzar-Aroca, R., Ramírez, A.I., Fernández-Albarral, J.A., Escribano, J., Zebrafish adamtsl4 knockout recapitulates key features of human ADAMTSL4-related diseases: a gene involved in extracellular matrix organization, cell junctions and development, 110572110572, Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Exp. Eye. Res.