Fig. 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250917-64
- Publication
- Tevar et al., 2025 - Zebrafish adamtsl4 knockout recapitulates key features of human ADAMTSL4-related diseases: a gene involved in extracellular matrix organization, cell junctions and development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
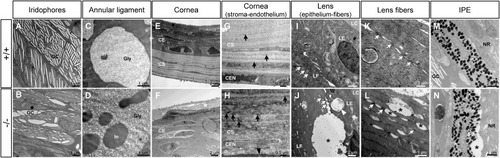
Transmission electron microscopy of the ocular anterior segment structures in adult (3-months-old) F3 adamtsl4 KO zebrafish. Tissue sections were prepared as described in the Materials and Methods section. Representative images of wild type (+/+) and KO (−/−) zebrafish are shown. A-B. Guanine crystals (GC) in iridophores. C-D. Glycoprotein aggregates (Gly) and cytoplasmic inclusions (In) in annular ligament cells. E-F. Cornea showing the thickened corneal epithelium (CE) and the necrotic superficial epithelial cell (white asterisk) in the KO zebrafish. G-H. Corneal stroma (CS) and endothelium (CEN). Note the contact between the CEN with the abnormal annular ligament in the KO zebrafish (black arrowhead). I-J. Lens epithelium (LE)-fiber (LF) interphase. K-L. Lens fibers. Gap junctions (white arrows). M-N. Iris pigment epithelium (IPE)-neuroretina (NE) interphase. Black asterisks: abnormal intercellular separations. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |
Reprinted from Experimental Eye Research, , Tevar, A., Aroca-Aguilar, J.D., Atiénzar-Aroca, R., Ramírez, A.I., Fernández-Albarral, J.A., Escribano, J., Zebrafish adamtsl4 knockout recapitulates key features of human ADAMTSL4-related diseases: a gene involved in extracellular matrix organization, cell junctions and development, 110572110572, Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Exp. Eye. Res.