- Title
-
A human Tau expressing zebrafish model of progressive supranuclear palsy identifies Brd4 as a regulator of microglial synaptic elimination
- Authors
- Bai, Q., Shao, E., Ma, D., Jiao, B., Scheetz, S.D., Hartnett-Scott, K.A., Ilin, V.A., Aizenman, E., Kofler, J., Burton, E.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Nat. Commun.
|
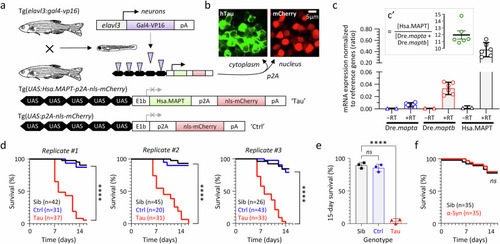
Reduced lifespan of transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau conditionally in neurons. |
|
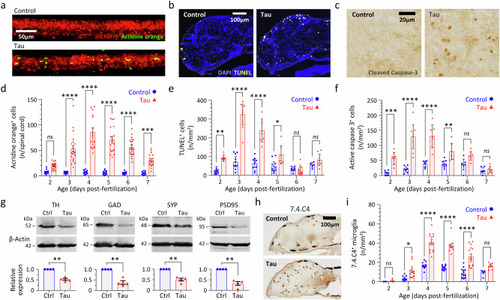
Neurodegeneration, synapse loss, and microgliosis in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. |
|
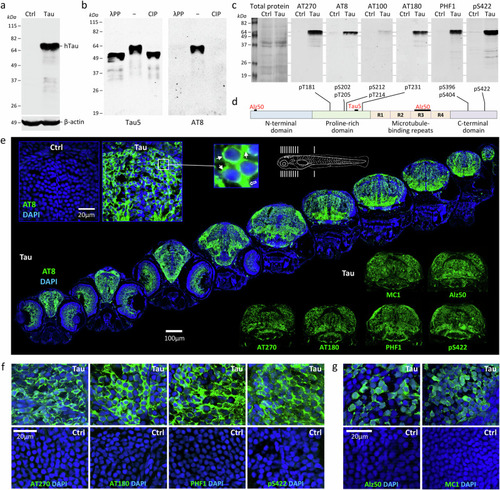
Human 4R/0N-Tau hyperphosphorylation, mislocalization and misfolding throughout the CNS of transgenic Tau zebrafish. |
|
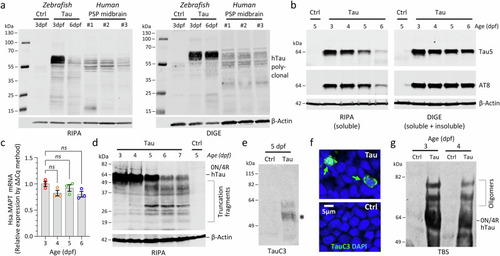
Loss of solubility, truncation, and oligomerization of Human 4R/0N-Tau in transgenic Tau zebrafish. Proteins were extracted from Ctrl or Tau zebrafish pooled head regions, using RIPA (SDS/Triton), DIGE (7 M urea) or TBS (tris-buffered saline) for analysis by western blot. |
|
Hypokinetic motor phenotype in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. |
|
Optokinetic reflex abnormalities in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. Optokinetic reflexes (OKR) were elicited at 5dpf and detected, measured, and analyzed using an automated tracking system |
|
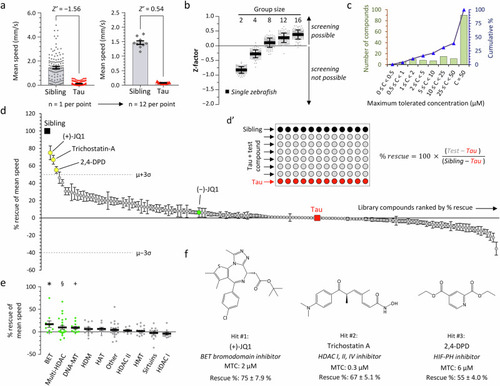
Small molecule screen to identify inhibitors of epigenetic readers, writer and erasers that rescue hypokinesia in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. |
|
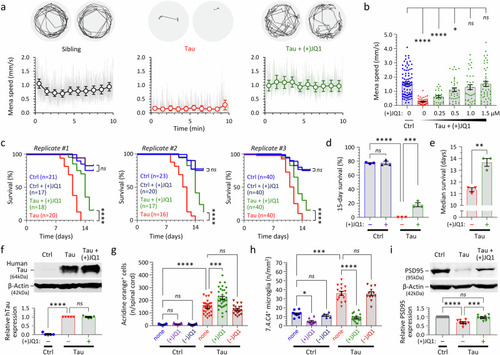
(+)JQ1 improves survival and rescues motor function, microgliosis, and expression of PSD95 in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. Zebrafish were exposed to repurchased (+)JQ1 or (−)JQ1 from 2dpf. |
|
(+)JQ1 inhibits microglial synaptic elimination in both transgenic zebrafish and rat primary culture models expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. |
|
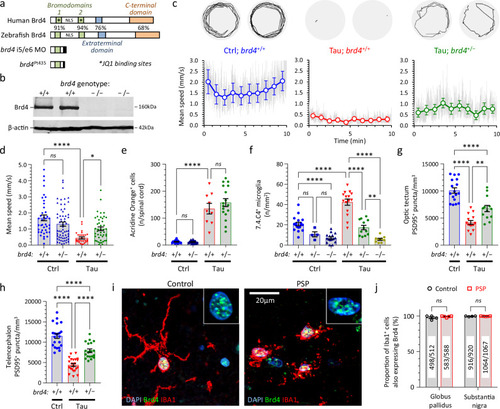
Brd4 regulates microgliosis and synaptic pruning in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 0N/4R-Tau and is expressed in human microglia. |