|
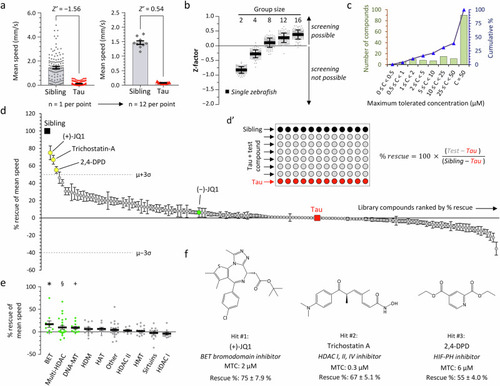
Small molecule screen to identify inhibitors of epigenetic readers, writer and erasers that rescue hypokinesia in transgenic zebrafish expressing human 4R/0N-Tau. a Mean speed during the light phase of the visual motor response (VMR) in non-expressing siblings (Sib; n = 115) and Tau zebrafish (n = 130). Data points show individual zebrafish on the left graph and means of groups of 12 zebrafish on the right; bars show group mean ± SE on both graphs. b Z-factor (Z’) was calculated from the primary data shown in panel a, either for single zebrafish, or for groups containing 2–16 zebrafish, each in 100 different random groupings. Points show different groupings at each group size, bars show mean ±2 SD. c Binned distribution (green bars, left scale) and cumulative % distribution (blue line, right scale) of the maximum tolerated concentration (MTC) of 147 small molecule modulators of epigenetic readers, writers, and erasers in larval zebrafish. d Screen of 147 small molecule modulators of epigenetic readers, writers, and erasers for rescue of VMR light phase hypokinesia in Tau zebrafish exposed to compounds at MTC from 2dpf to 5dpf. Rescue calculated as shown in inset d’. Data points show % rescue ±SE for each compound (n = 12 zebrafish per data point), ordered by rank along the x-axis (details in Supplementary Table 15). The untreated Tau (0% rescue; n = 12) and Sib (100% rescue; n = 12) groups are indicated. Library mean rescue ±3 SD is indicated; compounds satisfying the a priori definition of a ‘hit’ (library mean +3 SD) are shaded yellow and labeled. (−)JQ1, the inactive stereoisomer of (+)JQ1, is shaded green for comparison. e Data from panel (d) grouped by biological target. Bars show group mean ± SE; targets showing significant rescue across compounds within a group are shaded green (*p = 0.042, §p = 0.028, +p = 0.013, group mean vs. rescue = 0; 2-tailed, one sample t-test). BET bromo- and extra-terminal domain containing proteins, HDAC histone deacetylases, DNA-MT DNA methyltransferases, HDM histone demethylases, HAT histone acetyltransferases, HMT histone methyltransferases, Other, targets listed in Supplementary Table 17. f Chemical structures, molecular targets, maximum tolerated concentrations, and activities of the three ‘hits’ identified by the screen. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
|