- Title
-
Functional role for Taz during hindbrain ventricle morphogenesis
- Authors
- Dicipulo, R., Selland, L.G., Carpenter, R.G., Waskiewicz, A.J.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
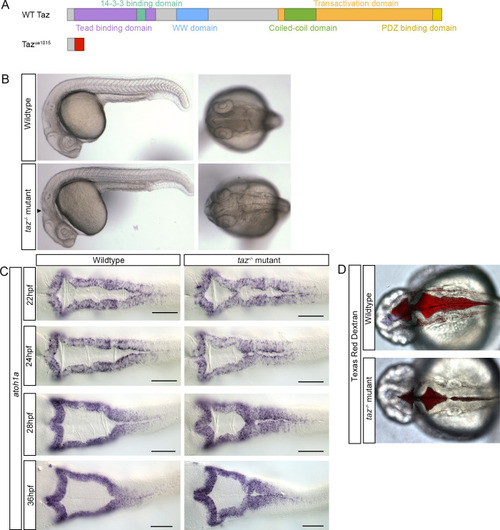
(A) Predicted transcripts of wild-type (top) and the TALEN generated |
|
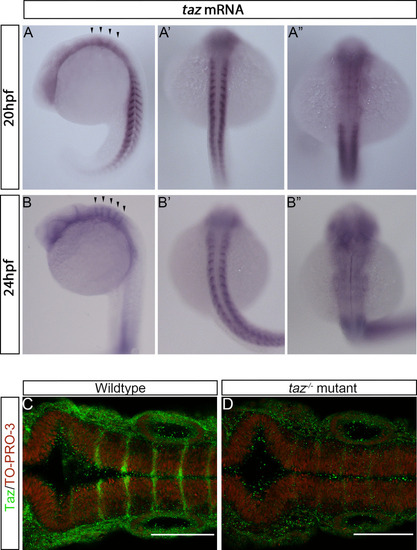
(A-A”). |
|
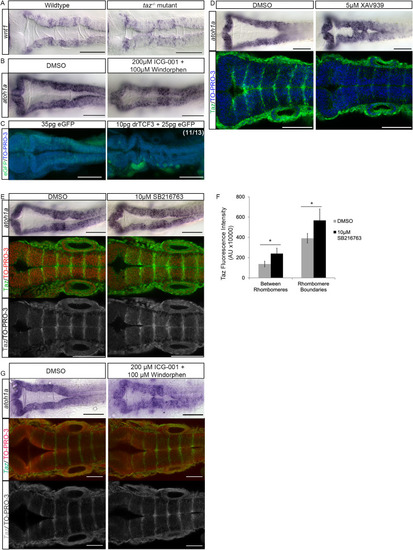
Wnt components are modified in β-catenin mediated transcription results in reduced ventricle size. (A) |
|
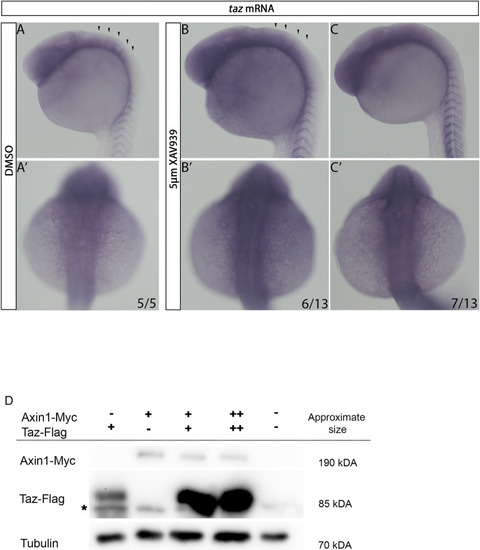
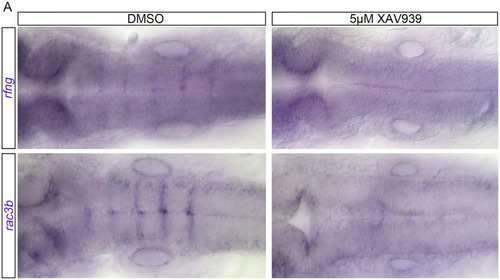
Wnt activity affects (A-C’) In DMSO treated animals, at 24 hpf |
|
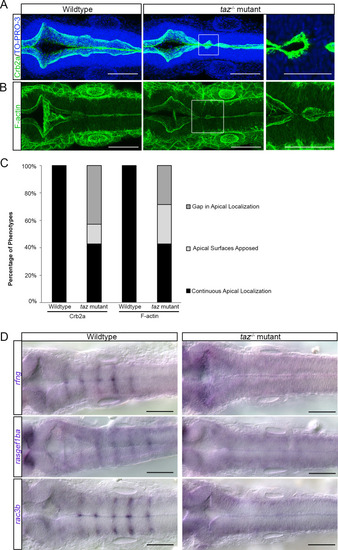
Apicobasal polarity components and patterned gene expression is perturbed in Changes to apicobasal polarity and cytoskeletal organization were assayed in wild-type and |
|
Wnt activity affects boundary cell gene expression. In DMSO treated animals at 24 hpf |