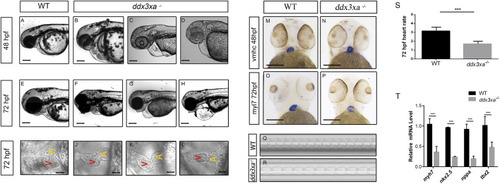
ddx3xa knockout induces early cardiac malformation and dysfunction in zebrafish. (A–H) Phenotypic analysis of zebrafish hearts. (A) Normal cardiac phenotype in wild-type (WT) zebrafish at 48 hpf. (B–D) Cardiac phenotypes in ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 48 hpf. (E) Normal cardiac phenotype in WT zebrafish at 72 hpf. (F–H) Cardiac phenotypes in ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 72 hpf. Scale bar: 500 µm (applies to A–H). (I) Dorsal view of the heart in WT zebrafish at 72 hpf. (J–L) Dorsal views of hearts in ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 72 hpf. Scale bar: 25 µm (applies to I–L). (M–N) Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) with vmhc probe at 48 hpf. ddx3xa−/− larvae display irregular ventricular contours compared to WT (scale bar: 250 μm). (M)vmhc WISH in WT zebrafish at 48 hpf. (N) vmhc WISH in ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 48 hpf. (O–P)myl7 probe WISH at 72 hpf. ddx3xa−/− larvae exhibit defective atrioventricular looping and atrial hypoplasia compared to WT (scale bar: 250 μm). (O)myl7 WISH in WT zebrafish at 72 hpf. (P)myl7 WISH in ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 72 hpf. (Q–T) Heartbeat analysis in WT and ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 72 hpf. (Q) Representative heartbeat trace of WT zebrafish at 72 hpf. (R) Representative heartbeat trace of ddx3xa−/− zebrafish at 72 hpf. (S) Statistical analysis of heart rate (n = 3; ***P < 0.001). (T) qRT-PCR analysis of myh7, nkx2.5, nppa, and tbx2 transcript levels in WT and ddx3xa−/− larvae at 72 hpf (n = 3; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
|

