- Title
-
Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 (CKAP4) affects podocyte cytoskeleton dynamics in diabetic kidney disease
- Authors
- Boi, R., Lassén, E., Johansson, A., Liu, P., Chaudhari, A., Tati, R., Müller-Deile, J., Schiffer, M., Ebefors, K., Nyström, J.
- Source
- Full text @ JCI Insight
|
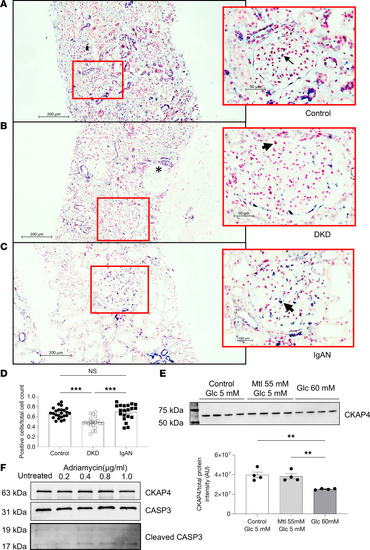
CKAP4 is downregulated in glomeruli in patients with DKD. CKAP4 mRNA was detected using in situ hybridization in control ( |
|
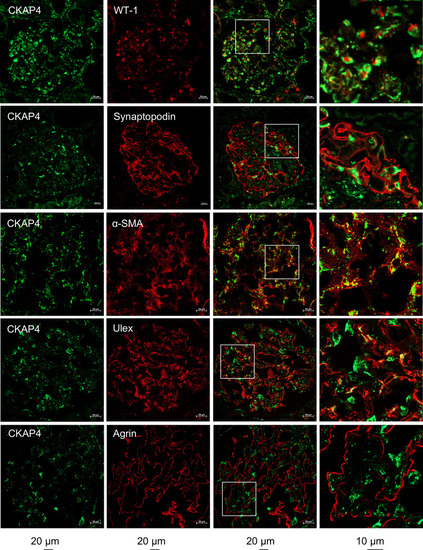
CKAP4 is expressed in all glomerular cell types in human glomeruli. Immunofluorescence staining of human kidney tissue for CKAP4 (green) and various markers for glomerular cells (red) to illustrate CKAP4 localization in the glomerulus. The first column shows CKAP4 staining. The second column shows, respectively: WT-1, marker for podocyte nuclei; synaptopodin, marker for podocyte foot processes; α-SMA, marker for mesangial cells; |
|
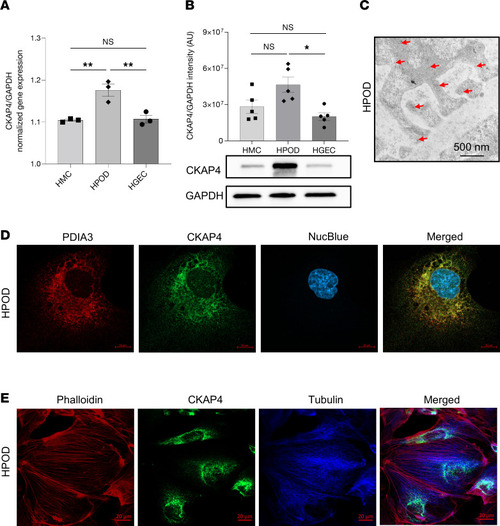
CKAP4 expression and localization in glomerular cells in vitro. CKAP4 gene expression was quantified with qPCR ( |
|
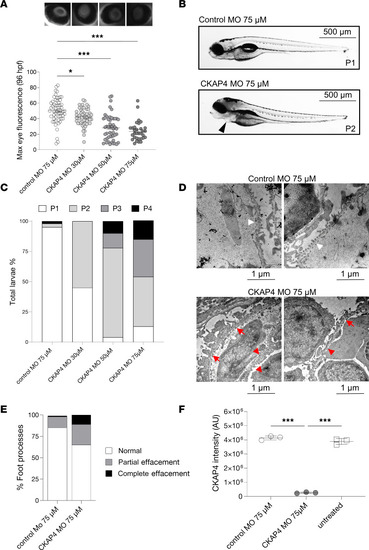
CKAP4 zebrafish homolog knockdown causes proteinuria and podocyte FPE. CKAP4 was knocked down in zebrafish using MO in different concentrations, 30, 50, and 75 μM MO. Proteinuria was measured by reduction of eye fluorescence ( |
|
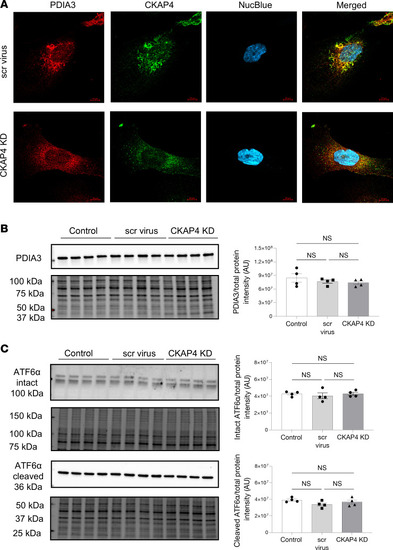
CKAP4 KD in vitro influences the shape of the ER in HPODs. Immunofluorescence staining of the ER marker PDIA3 in scr control and CKAP4 KD HPODs. Scale bars: 10 μm. ( |
|
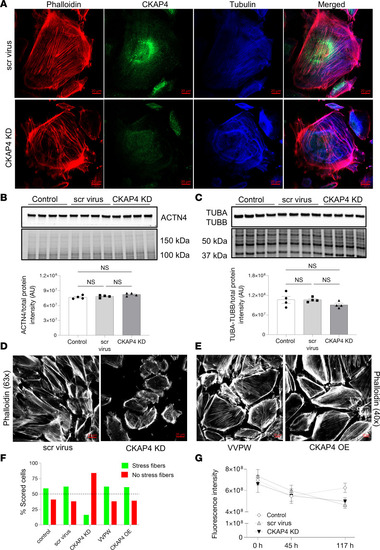
CKAP4 KD in HPODs in vitro alters the cytoskeleton. Immunofluorescence staining of HPODs with phalloidin (red, actin fibers), tubulin (blue, microtubules), and CKAP4 (green) in scr control and CKAP4 KD. HPODs showed loss of actin stress fibers and rearranged microtubules ( |
|
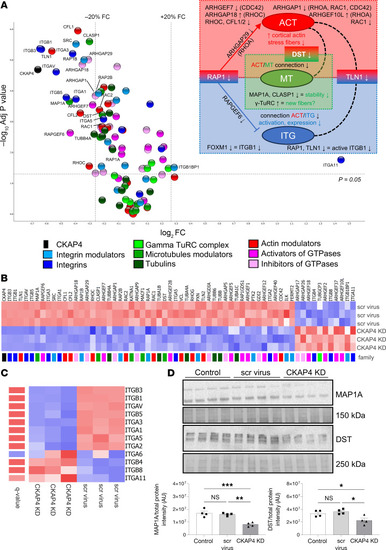
CKAP4 KD influences protein families related to cytoskeleton dynamics. Volcano plot of selected proteins from the proteomic analysis of CKAP4 KD versus scr-treated HPODs. Dotted lines represent the |
|
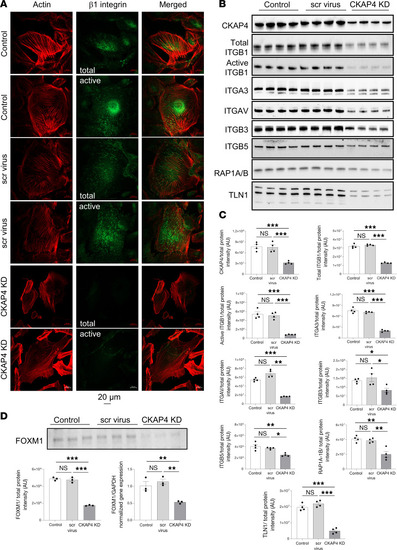
CKAP4 KD causes downregulation of integrins and influences their modulation. Immunofluorescence images of HPODs (untreated, scr-treated control, and CKAP4 KD cells) with phalloidin (actin cytoskeleton, red) and total and active β1 integrins (green) ( |