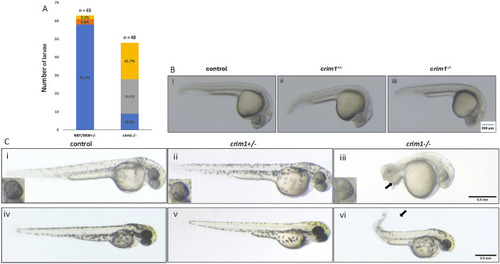
Morphology and appearance of control, heterozygous, crim1+/−, and crim1−/− larvae that are homozygous for a 2 base pair deletion, c.339_340delCT p.Leu112Leufs*3 at 24, 48, and 72 h post fertilization (hpf). (A) Morphology for control (n = 63) and crim1−/− larvae (n = 48) that are homozygous for a 2 base pair deletion in crim1. The columns are colored according to the numbers and percentages of larvae with a normal phenotype (blue), mild deformity (orange), curved body axis (yellow), and malformations such as edema, cardiac defects, and severely shortened body (gray). The crim1−/− larvae have an increased rate of abnormalities compared to controls. (B) Representative photographs of control larvae (panel i), heterozygous crim1+/− larvae (panel ii), and homozygous crim1−/− larvae (panel iii) at 24 hpf. The heterozygous crim1+/− larvae and homozygous crim1−/− larvae appear similar to the control. (C) Representative photographs of control larvae (panels i and iv), heterozygous crim1+/− larvae (panels ii and v), and homozygous crim1−/− larvae (panels iii and vi) at approximately 38 hpf (panels i, ii, and iii) and 72 hpf (panels iv, v, and vi). The heterozygous crim1+/− larvae appear similar to controls, but the homozygous crim1−/− larvae show shortened body axes and curved tails at both time periods, as indicated by the arrows. Scale bars = 500 µm.
|

